Numerous industries have seen notable advancements in artificial intelligence. Systems that closely resemble human intelligence in terms of behavior and traits are able to learn, reason, and comprehend tasks in order to act.
Understanding the various artificial intelligence concepts that aid in problem-solving in the real world is crucial. This can be accomplished through the use of procedures and methods such as machine learning, which is a branch of artificial intelligence.
The main branches of artificial intelligence will be covered in this article.
To avoid AI detection, use Undetectable AI. It can do it in a single click.
Table of Contents
The Top 7 Branches of Artificial Intelligence
Computer Vision
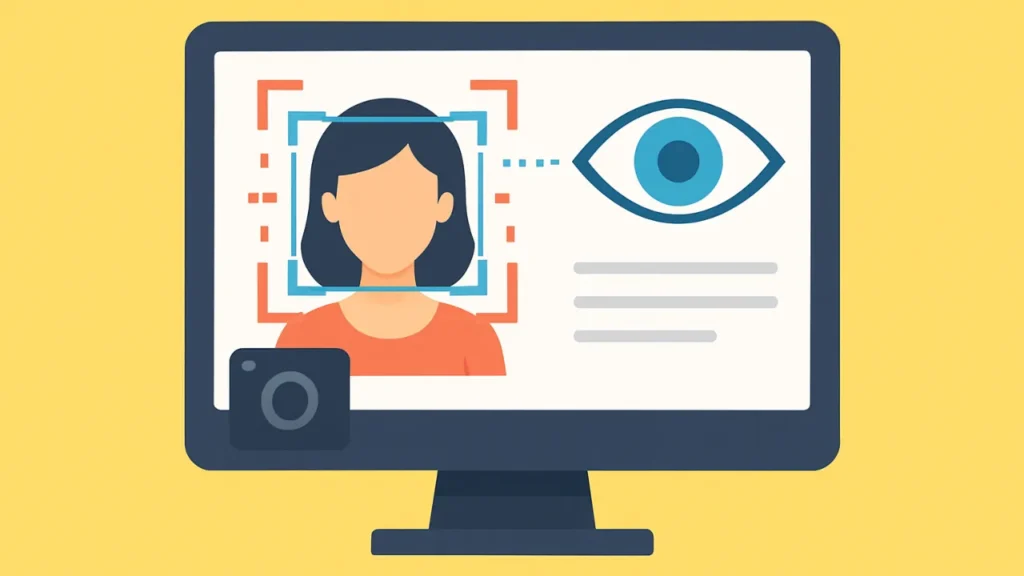

The objective of computer vision, one of the most well-known areas of artificial intelligence at the moment, is to create methods that help computers see and comprehend digital images and videos. Computers can recognize objects, faces, people, animals, and more by applying machine learning models to images.
With sufficient data fed through a model, computers can learn to differentiate between different images. Algorithmic models aid computers in learning the contexts of visual data. Together with a model, a convolutional neural network deconstructs images into pixels and assigns labels or tags to them.
The neural network then performs convolutions—a mathematical operation on two functions—using the labels to generate a third function and generate predictions about what it observes.
Fuzzy Logic
One method for resolving problems or statements that may or may not be true is fuzzy logic. This approach mimics human decision-making by taking into account every possible result between the digital “yes” and “no” values. In other words, it gauges how accurate a hypothesis is.
This area of artificial intelligence is used for reasoning about ambiguous subjects. It’s a practical and adaptable method of applying machine learning techniques and rationally replicating human thought.
Fuzzy logic, which depends on the acceleration, speed, and wheel speed of each individual car, is used by companies such as Nissan to control breaks in hazardous situations.
Expert Systems
Like a human expert, an expert system is a program that specializes in a single task. The primary purpose of these systems is to solve complex issues with decision-making abilities similar to those of humans. They employ a set of guidelines termed inference rules that are defined for them by a knowledge base that receives data.
If-then logical concepts can be used to solve complicated problems and assist with loan analysis, virus detection, information management, and more. The success of artificial intelligence was significantly aided by the development of the first expert system in the 1970s.
CaDeT, a diagnostic support system that can assist medical professionals by identifying cancer in its early stages, is an example of an expert system.
Robotics
Robots are machines that have been programmed to perform intricate sequences of tasks automatically. They can be operated by people using external devices, or they can have internal control systems. Robots assist people with repetitive and tiresome tasks.
Particularly, AI-powered robots can support space exploration for organizations like NASA. The most recent advancements and well-known instances of robotic evolution are humanoid robots. Hanson Robotics created Sophia, a robot that uses neural networks and artificial intelligence to function.
She is able to interact with people and recognizes their faces, emotions, and gestures. Typical applications of robotics in daily life include manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and other sectors.
Machine Learning

One of the more challenging areas of artificial intelligence is machine learning, which is the capacity of machines to automatically learn from data and algorithms. Without being explicitly programmed to do so, machine learning can make decisions and use prior experiences to improve performance.
In order to construct logical models for future inference, the process begins with the collection of historical data, such as direct experience and instructions. Data size affects output accuracy; more data will create a better model, which will raise the accuracy of the model.
Deep Learning/Neural Networks
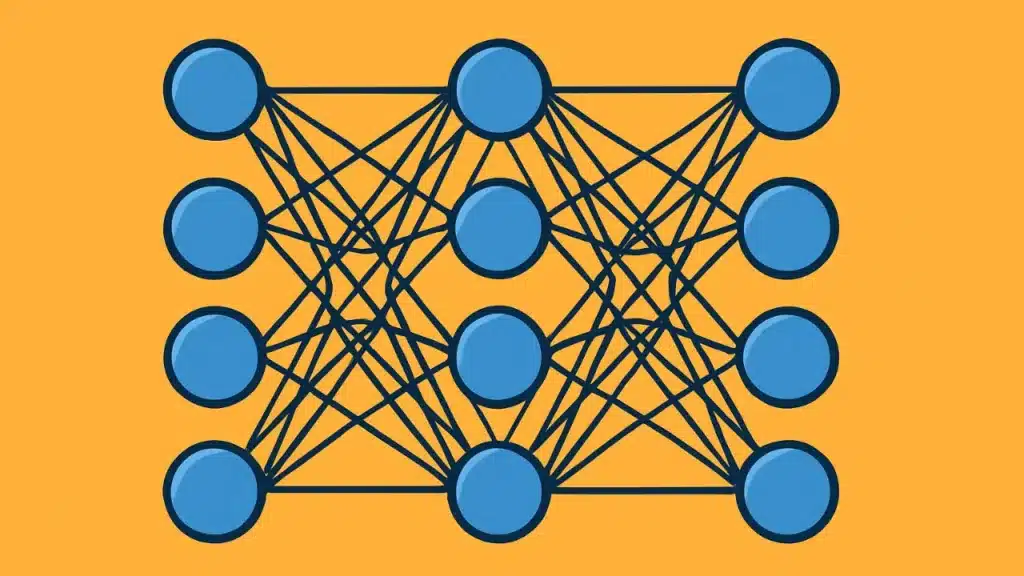
Other names for neural networks include simulated neural networks (SNNs) and artificial neural networks (ANNs). Neural networks, the brain’s model for deep learning algorithms, mimic the way biological neurons communicate with one another.
The node layers of an ANN are made up of an output layer, one or more hidden layers, and an input layer. A threshold and weight are assigned to each node, commonly referred to as an artificial neuron, which connects to other neurons.
Data transmission to the subsequent network layer is initiated when a node’s output surpasses a predetermined threshold value. For neural networks to learn and become more accurate, they require training data.
Language Processing

Computers can comprehend spoken and written language just as well as humans due to natural language processing. Computers can process human language in voice or text data to fully comprehend the meaning, intent, and sentiment by combining machine learning, linguistics, and deep learning models.
For instance, voice data is consistently transformed into text data in speech recognition or speech-to-text. Because people speak with different accents, intonations, and levels of emphasis, this can be difficult. In order for computers to comprehend and identify data right away, programmers must teach them natural language-driven applications.
Conclusion: Branches of Artificial Intelligence
The connections between these branches of artificial intelligence (AI) became evident. Improvements in one area can result in improvements in another, and each branch supports the others.
For example, advances in computer vision can help robotics, and machine learning can improve natural language processing. It is probable that the various branches of artificial intelligence (AI) will keep expanding and changing, creating new opportunities.
Emerging domains like explainable AI and ethical AI, which concentrate on increasing the accountability and transparency of AI systems, are already visible. Studying these areas demonstrates how technology affects our lives in addition to assisting us in understanding it.
AI has the ability to simplify tasks, increase productivity, and resolve challenging issues. It is essential that we handle AI responsibly as we proceed. We can use AI to everyone’s advantage if we talk about its implications and make sure it develops ethically.
FAQs: Branches of Artificial Intelligence
What are the main branches of artificial intelligence?
The main branches of artificial intelligence include machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), robotics, computer vision, and expert systems. Each branch contributes to the development of AI technologies that mimic human-like intelligence and solve real-world problems.
How does machine learning relate to artificial intelligence?
Machine learning is a key branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on the development of algorithms and models that enable computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without explicit programming.
What is the role of neural networks in AI?
Neural networks, particularly artificial neural networks, are computational models inspired by the human brain. They are used in various AI applications, including deep learning, to process large amounts of data and make decisions based on that data.
What is natural language processing (NLP)?
Natural language processing (NLP) is a branch of AI that enables computers to understand, interpret, and process human language. It is used in applications like chatbots, virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, and sentiment analysis.
How do AI models use reinforcement learning?
Reinforcement learning is a subfield of AI where models learn to make decisions by interacting with their environment. They receive feedback in the form of rewards or penalties, allowing them to improve their decision-making abilities over time.
What is the significance of computer vision in AI?
Computer vision is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on enabling computers to interpret visual information from the world. This includes tasks like facial recognition, image recognition, and identifying objects in images and videos.
Can AI systems perform tasks autonomously?
Yes, AI systems can perform tasks autonomously. For instance, self-driving cars utilize various AI technologies, such as computer vision and machine learning, to navigate the environment without human intervention.
What are generative AI and its applications?
Generative AI refers to models that can generate new content, such as images, text, or music, based on training data. Applications include creating art, writing articles, and developing realistic virtual environments.
How does fuzzy logic contribute to AI?
Fuzzy logic is used in AI systems to handle uncertainty and reason in a way that mimics human decision-making. It allows machines to make inferences based on imprecise or vague information, improving problem-solving capabilities.
What is the future of artificial intelligence?
The future of AI holds great potential, with advancements in AI applications, edge AI, and AI tools that enhance human intelligence. As AI continues to evolve, it will increasingly impact various industries and everyday life.
Read Also >>> Goals of Artificial Intelligence in 2025


